Different Battery Chemistries
All recommendations are for building GNOR race boats. You may use this as a guide for other projects.
Listed bellow are a few of the common battery chemistries that you may use to power your boat. Some of these are much more recommend than others but this will cover all of the common ones.
Lithium
Please read up on the following topics if you intend on using ANY lithium battery chemistries:
- Lithium battery safety
- Lithium battery charging
Lithium Polymer (Lipo) [Recommended]
LiPo
Lithium Polymer batteries are the most recommended for the boat race. These batteries are available for relatively low prices from Amazon and even local hobby retailers.
Lipo batteries are very power dense compared to their cousins, meaning per unit mass they can output much more energy at one time. This leads them to be really good for small scale high output electronics applications like the boat project.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Easy to find
- High power output
- Come with many different common battery connectors
Cons:
- Easy to damage
- Heavier than some other lithium chemistries
Common form factors
Lipo batteries are found in the form of pouch cells, these cells are soft sided and easy to damage so be careful when using them.
Battery voltage
Each cell will run around 4.2v when fully charged and 3.7v when at 80% DOD.
Battery packs
When searching for Lipo battery packs you will want to use a battery power calculator to determine the capacity you will need. You will also want to look at the maximum voltage of your motor to determine the number of cells you need in a battery pack.
Hard Sided Packs: these are great because you get an extra layer of protection
Standard Heatshrunk Packs: these are the most common and cheapest
Lithium Ion (Li-Ion) [Secondary]
Li-Ion
Lithium Ion batteries are a very good choice for small electronics projects. These batteries are more energy dense than almost all other types of batteries listed. Which means by unit of mass these batteries hold the most energy.
One of the big downsides of these batteries is they often need to be made custom.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Most energy dense (lightest weight battery)
- Very configurable
Cons:
- Assembly most likely required
- Cost
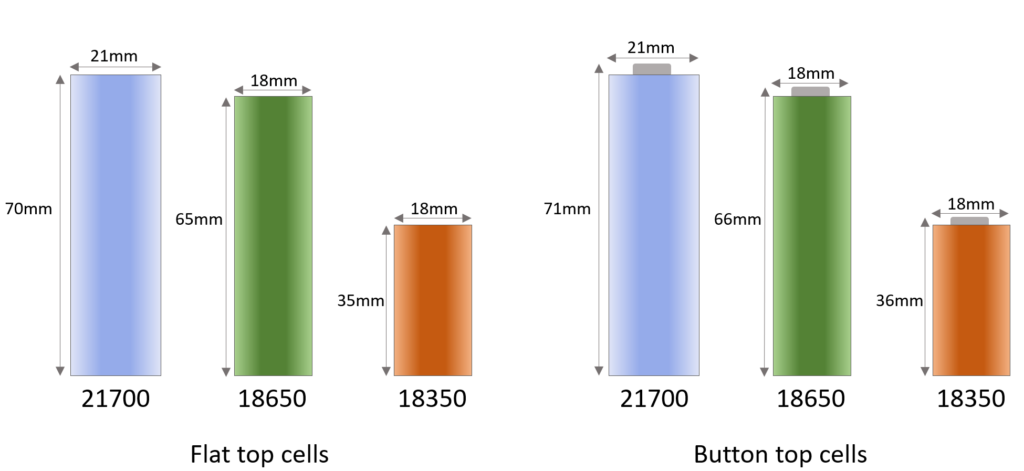
Common form factors
Battery voltage
With Lithium Ion, the cells are generally 4.2v when fully charged and 3.2v when at 80% DOD.
Battery packs
In most cases you will need to make the battery packs yourself out of the cells they are sold in. This can be an extremely dangerous process if you don't know what you are doing!
Do not attempt to make battery packs if you don't already have experience or you have not consulted a TA or Robotics club member!
If you decide to build your own battery pack I recommend talking to someone in the Robotics club or the TI lab about helping make your battery pack.
If you do find premade battery packs they are a good alternative to the recommended Lipo
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFe) [Secondary]
LiFe
Lithium Iron Phosphate is one of the newest mainstream lithium battery chemistries on the market. These are now the most common battery chemistry in electric vehicles as it is a much less reactive chemistry to other lithium so it is safer. This increase in safety come at a cost to energy density. So this battery is slightly heavier than Li-Ion.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Safer
- High power output
Cons:
- Slightly decreased energy density
- Cost
- Assembly may be required
Common form factors
Battery voltage
With Lithium Iron Phosphate, the cells are generally 3.65v when fully charged and 3.2v when at 80% DOD.
Battery packs
One form factor you may find LiFe battery packs in regular lead acid sizes be cause they are an almost drop in replacement for lead acid charging and voltage.
You may need to make the battery packs yourself out of the cells they are sold in. This can be an extremely dangerous process if you don't know what you are doing!
Do not attempt to make battery packs if you don't already have experience or you have not consulted a TA or Robotics club member!
If you decide to build your own battery pack I recommend talking to someone in the Robotics club or the TI lab about helping make your battery pack.
Other Chemistries
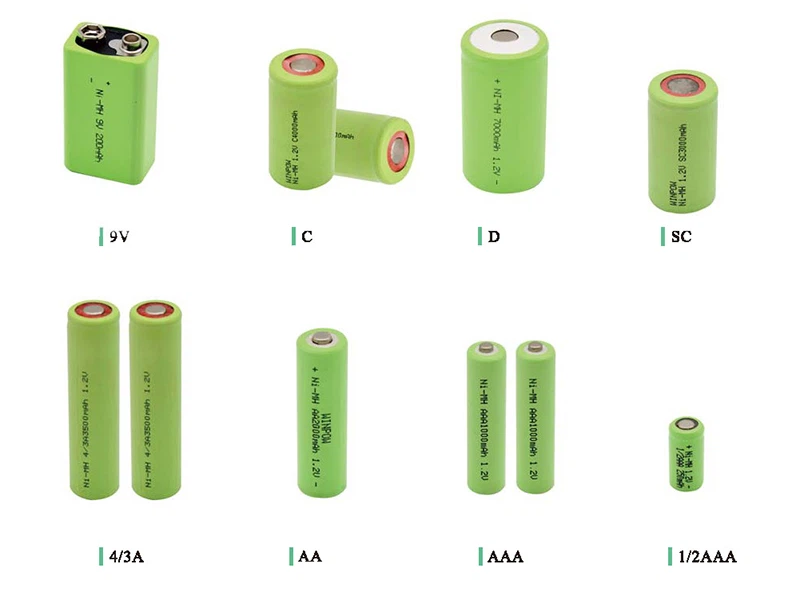
Nickel Metal Hydride/Cadmium (NiMH/NiCd) [Not Recommend]
NiMH / NiCd
Nickle metal hydride/cadmium batteries are what you would commonly know as rechargeable AA's & AAA's. These batteries are great for low power every day use items like TV remotes and kids toys. These are not great for high power applications.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Easy to find
- Very common form factor
Cons:
- Bad for high power applications
- Low capacity
Common form factors
Battery voltage
These batteries are around 1.2v.






No Comments